Mining is used to extract many highly used resources in the world today. Mining unveils valuable minerals like coal, which is a source of electricity and heat, as well as in the manufacturing of cement and steel. As such, these minerals must be mined to supply the high demand for this resource, and there are many ways to do so.
Most mining operations combine different methods to extract minerals most efficiently. Initially, the mineral closer to the surface would be mined using a surface mining method. After the minerals have been exhausted that way, the coal found deeper in the seam would be mined using an underground mining method. This allows for the most minerals in an area to be extracted, using the most efficient methods.
The type of mining is based off of a variety of factors. The thickness and depth of the coal seam are very important in deciding which method will be used, as well as the terrain that is found on the surface above the coal. Economic factors also come into play, as some methods are more or less costly than others.
Below are seven different types of mining processes:
1. Surface mining
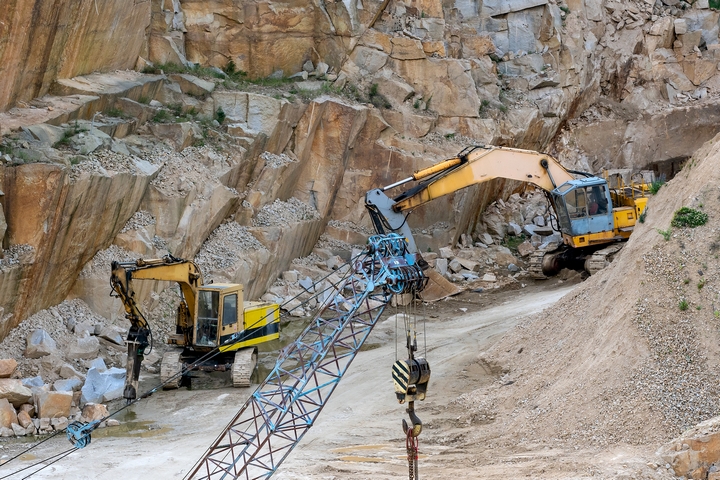

There are two main types of mining – every method can be divided into either surface or underground. Logically, surface mining is used to gain access to minerals located closer to the earth’s surface. The place where minerals can be found is often called a seam. A seam is considered shallow if it is located closer to the earth’s surface, and deep if it is located further away.
2. Underground mining
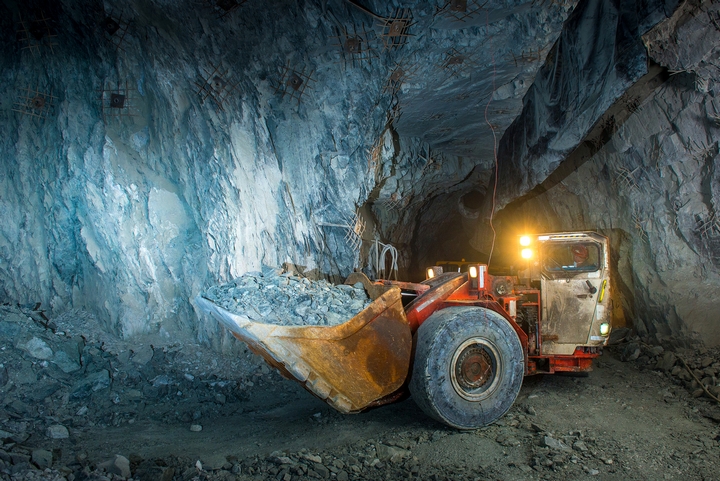

Underground mining can be used for minerals in more shallow seams, but is more often used for deeper deposits. In order to access the minerals underneath, blasting is done. Blasting is an key part of surface mining, as it helps to prepare the terrain for mining. The rocks are broken up using explosives, and then cleared away using machinery.
3. Shaft mining

Also called shaft sinking, this method consists of any underground mining method that uses a tunnel that heads straight down to wherever the ore is located.
The shaft may be an exact vertical or a near vertical drop into the mine, and an elevator or lift is installed to bring workers into and out of the mine. The mine will extend from this initial spot in all directions.
4. Open cast mining
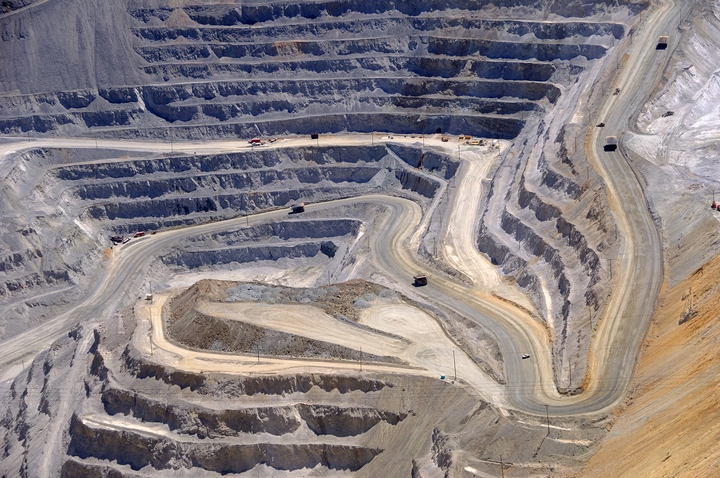

Also known as open pit mining, this is a method of surface mining where a large pit is made in the ground, and the coal is mined directly from that pit. This is a great method to use for a shallow coal seam and it is extremely productive.
Of all the types of mining, this is one of the safest processes. It doesn’t require very much specialized equipment, unlike some other methods.
5. Longwall mining
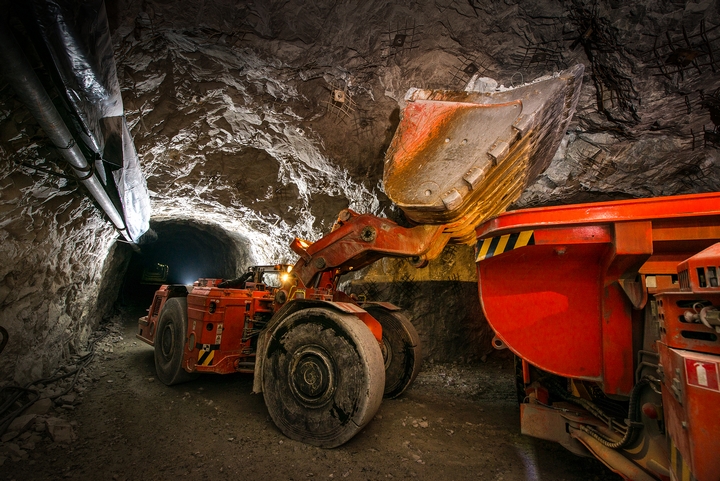

Using specialized machines, longwall mining is an underground mining method that cuts out panels of the coal, which are then sheared down and brought to the surface. This method is highly mechanized, and is therefore a very safe type of mining.
It is a highly productive method as well, with a very low cost per ton as compared to some other methods. However, longwall mining does require highly specialized machinery, which can be very costly to start off. It also doesn’t allow for very great selection of the grade of the ore.
6. Room & pillar mining
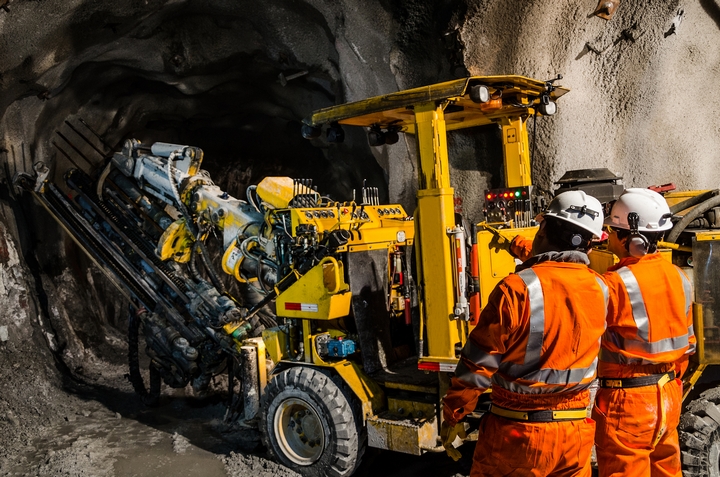

The title given to room and pillar mining is very fitting, as it is an underground method of clearing out coal by creating roomlike spaces. Some material is left in pillars, which helps to support the roof so that ore around it can be removed.
These types of mining offer good ventilation – a sought after feature in underground mining – and high productivity. It’s not a very flexible method, and doesn’t offer a lot of selectivity, however it is better than some other methods. The room and pillar method does, however, limit the depth at which the ore can be mined.
7. Hydraulic mining

Hydraulic mining uses water to break the ore away and carry it to the surface. In underground mining, one of the most difficult problems to solve is how to get the coal back up to the surface.
With hydraulic coal mining, water is pushed at high pressure against the ore’s surface, breaking away the chunks bit by bit. The water, with the bits of coal in tow, are then pushed through a pipe to the surface, where the coal is filtered out of the water.
One of the major advantages of hydraulic coal mining is that the water minimizes the chances of fire and explosion, and it reduces the amount of dust, making it a safer and more healthy working environment. However, power consumption for these types of mining is very high.