As we grow older, walking can become more challenging. Understanding the causes of walking issues in older adults can help caregivers, family members, and seniors take proactive steps to maintain mobility and independence.
Understanding the causes of walking issues in older people empowers seniors and caregivers to take proactive measures for better mobility and quality of life. By addressing these factors through regular exercise, proper medical care, and creating a safe living environment, seniors can navigate walking challenges and maintain their independence.
Let’s explore the common reasons behind mobility challenges and learn how to address them.
1. Muscle Weakness
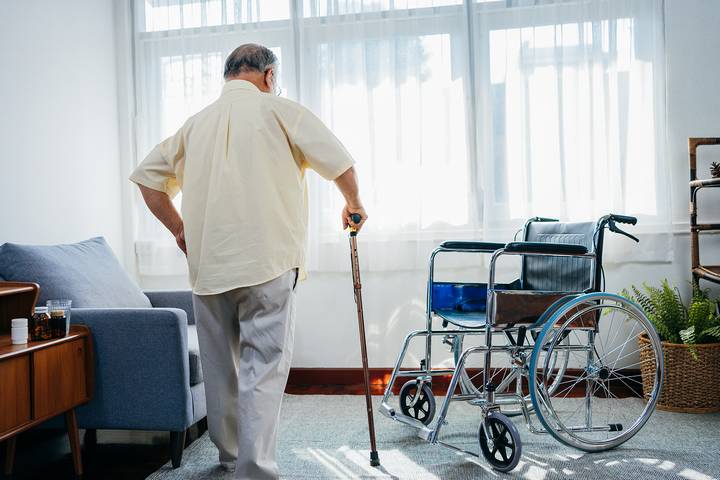

Aging can cause our muscles can weaken. Muscle weakness can cause wobbly steps and difficulty supporting the body’s weight. This might lead to slower walking and a higher risk of falls. Regular exercise, especially strength training, helps keep muscles strong and supports better walking.
By staying active, you can give your muscles the boost they need, making walking a smoother and safer experience as you age.
2. Joint Pain and Arthritis
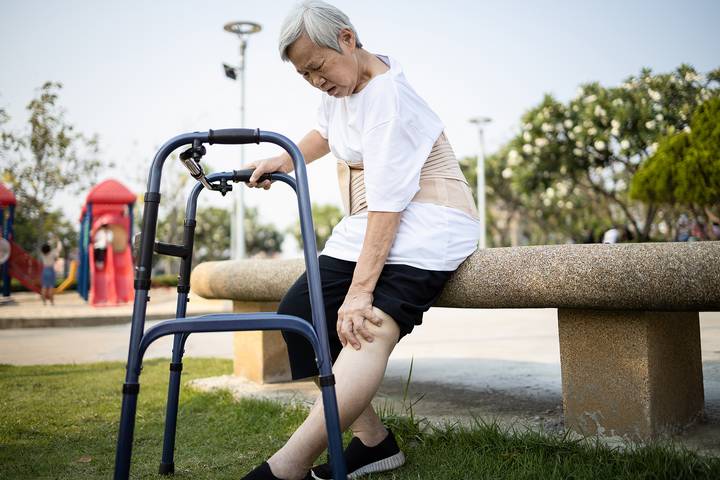

Joint pain and arthritis become more common as we age. These issues can make joints stiff and achy, affecting your walking stride. Arthritis might cause discomfort and slow you down, making each step harder. Staying active with gentle exercises and stretches that keep your joints moving is essential.
Talk to a doctor or physiotherapist who can help you manage the pain and find ways to make walking more comfortable.
3. Balance and Coordination Issues
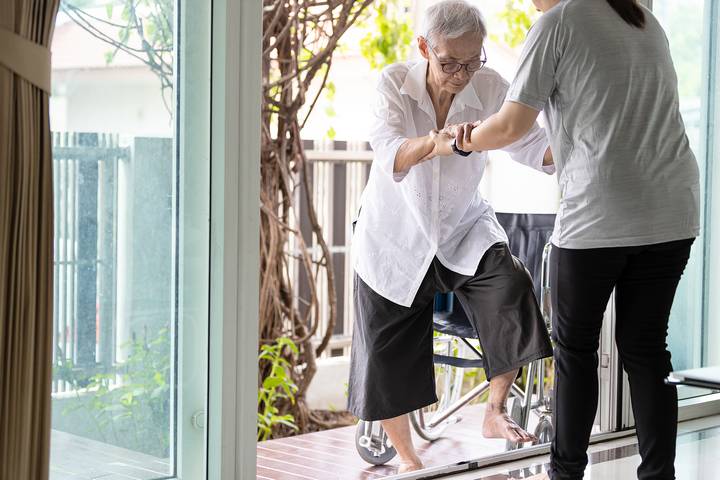

Reduced sensory input and changes in the inner ear’s function can impact balance and coordination, leading to walking difficulties. These issues might make you feel unsteady, leading to stumbling or falls.
Walking might become slower and less steady, making everyday tasks harder. Balance-enhancing exercises, such as yoga or simple weight-shifting routines, can help improve stability. Walkers for seniors can also offset balance and coordination issues.
4. Neurological Conditions
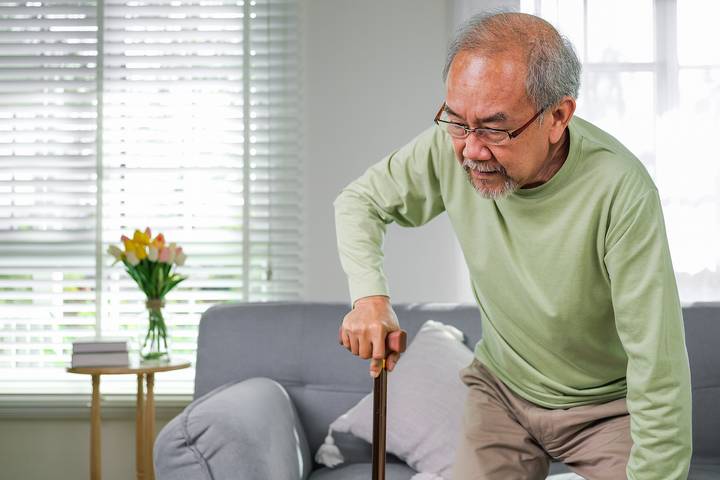

Conditions like Parkinson’s disease or stroke can affect nerve signals that control walking. They might cause shaky steps, slower movement, or trouble with balance. These changes can impact your walking ability and make your gait much less smooth.
Physical therapy and targeted exercises may aid in maintaining or regaining mobility in consultation with a healthcare provider.
5. Medication Side Effects

Certain medications can sometimes cause side effects, leading to dizziness, weakness, or instability. These effects can make walking feel more difficult or risky. Talk to your healthcare professional about your medications and any potential side effects you may experience. They can help adjust your treatment plan if needed.
6. Foot Problems

Foot problems that become more common with age can affect how seniors walk. Conditions like bunions, pain, or ill-fitting shoes can lead to discomfort and changes in walking patterns. These issues might slow you down or make steps less steady.
Properly fitting shoes, orthotics, and regular foot care can help alleviate problems. By paying attention to your feet and addressing any issues, you can maintain mobility as long as possible.
7. Vision Impairment

As we age, vision changes can affect how we walk. Poor eyesight might make it harder to see obstacles or judge distances, leading to unsteady steps. Reduced visual awareness can increase the risk of falls. Regular eye check-ups, proper eyewear, and well-lit environments can help seniors walk safely.
Staying vigilant about eye health ensures seniors can confidently navigate their surroundings and maintain mobility as they enjoy daily activities.
8. Chronic Diseases
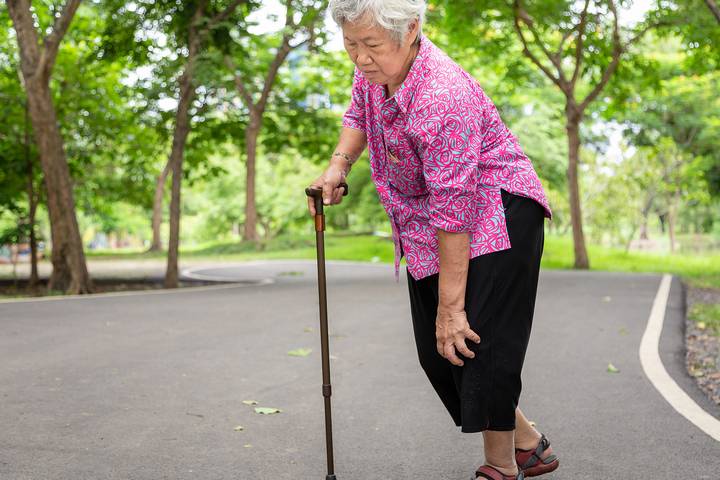

Long-term health issues can impact walking for older adults. Conditions like diabetes or heart problems might affect strength and balance, making walking more challenging. The discomfort caused by these and other chronic issues can slow down steps or make movement less steady.
Managing these conditions with a doctor’s guidance, treatment, and exercises tailored to your abilities can help keep you moving.
9. Cognitive Decline
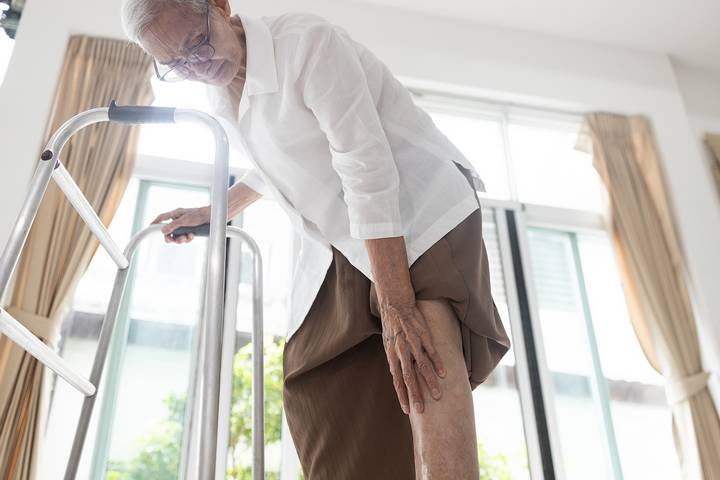

Cognitive decline, like dementia, can affect how seniors move. It might cause confusion or slower reactions, making walking less steady. This could lead to a higher risk of falls. To stay safe, caregivers should provide support and create a secure environment.
Engaging in gentle exercises or supervised walks can help maintain mobility. Recognizing the connection between the mind and body is key to keeping seniors moving comfortably. By adapting activities and ensuring a safe setting, we can help seniors maintain their independence and enjoy a fulfilling, active life despite cognitive challenges.
10. Fear of Falling
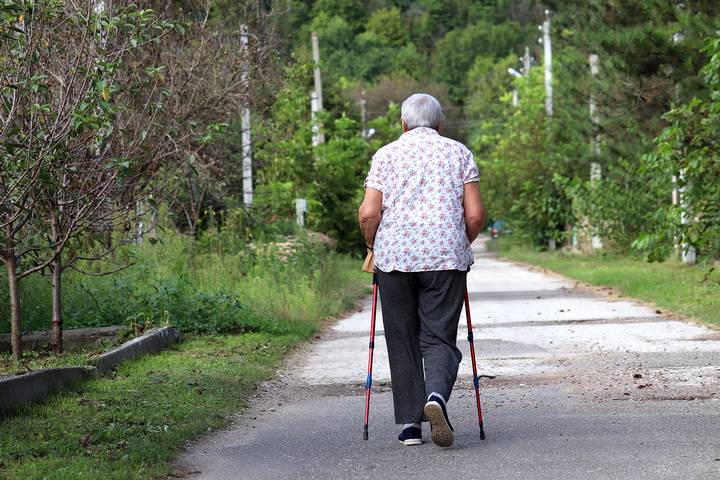

Previous falls or fear of falling can lead to cautious, hesitant walking patterns. Older adults might walk cautiously or avoid certain activities when worried about falling. This cautiousness can lead to weaker muscles and reduced mobility.
To overcome this fear, seniors can practice exercises that improve balance and strength. Creating a safe living environment and using assistive devices can also boost confidence. By addressing the fear of falling, seniors can regain their sense of security, move more freely, and enjoy an active and independent lifestyle.